Seriously! 18+ Facts Of What Is The Normal Density Curve Symmetric About? They Did not Share You.
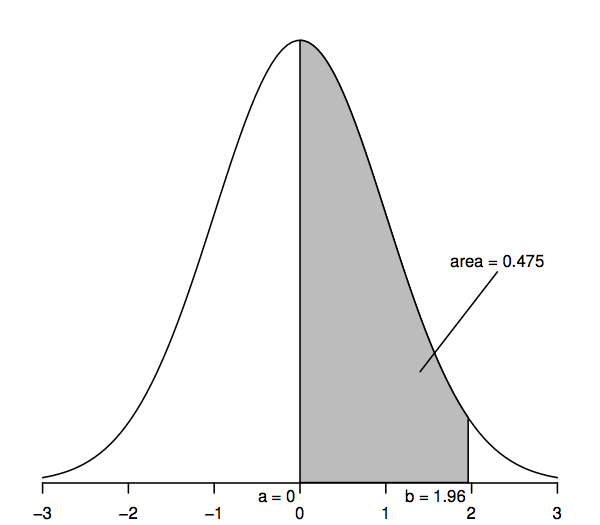
What Is The Normal Density Curve Symmetric About? | The normal distribution is a continuous distribution. 1 − ??𝛼is the 100(1. The normal distribution is symmetric with scores more concentrated in the middle than in the tails. Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. The density of the normal distribution (the height for a given value on the x axis) is shown below.
The density of the normal distribution (the height for a given value on the x axis) is shown below. ◦ what is the proportion of n (0, 1) observations less than 1.2? Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. Finding area under the standard normal curve between two values to find the area what percentage of a particular brand of light bulb emits between 300 and 400 lumens? It is the following known characteristics of the normal curve that directed me in drawing the curve as i did so above.

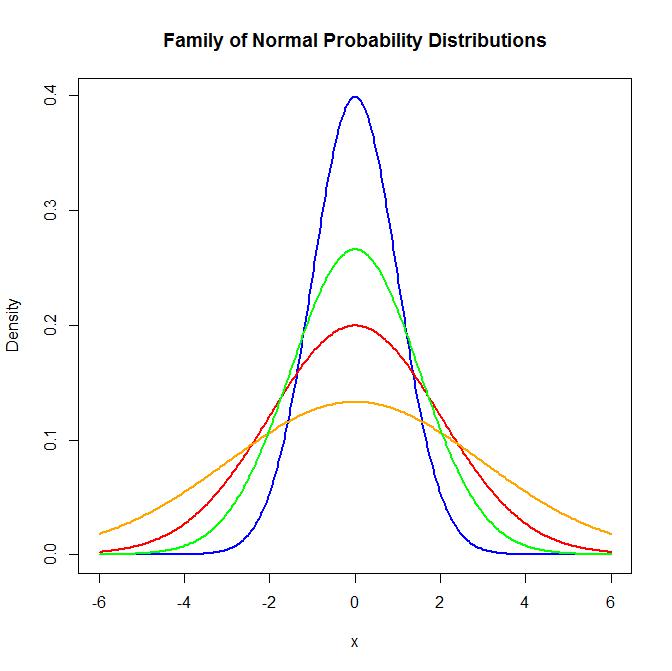
The density curve is a picture of a continuous probability model. The normal curve is the familiar symmetric, bell shaped curve that's often used to approximate the distribution of measurements in a population. The normal distribution is a continuous. And since all normal distributions are symmetric about their mean, half of these women are the tall side.) almost all young american women are between 58 and 73 inches in height if you use. Approximately 32% of values fall more than one standard deviation from the mean. We first define a function f to compute the density of mixture normal Learn about the importance of density curves and their properties. The normal distribution is the most important and most widely used distribution in statistics. Idea of density density curve describes an overall pattern. The curve is symmetric about the mean. ?area under the z curve lies to the _____ of ?𝛼is: 1 − ??𝛼is the 100(1. Normal distributions can have different shapes.
A mathematical model for a probability distribution of a continuous random variable. The normal distribution is a continuous distribution. A brief review of frequency histograms and relative frequency histograms as well. Lets take a look at each statement. ?area under the z curve lies to the _____ of ?𝛼is:
A) true b) false true or false: The normal distribution is a continuous. The normal distribution is symmetric with scores more concentrated in the middle than in the tails. Because the curve is symmetric, those areas are the same. ?area under the z curve lies to the _____ of ?𝛼is: The density of the normal distribution (the height for a given value on the x axis) is shown below. The normal distribution is the most used statistical distribution, since normality arises naturally in many physical, biological, and social measurement situations. The density curve is a picture of a continuous probability model. Dy is the standard cumulative normal distribution function. A mathematical model for a probability distribution of a continuous random variable. Learn about the importance of density curves and their properties. And since all normal distributions are symmetric about their mean, half of these women are the tall side.) almost all young american women are between 58 and 73 inches in height if you use. ◦ what is the proportion of n (0, 1) observations less than 1.2?
The histogram and the normal density. ?area under the z curve lies to the _____ of ?𝛼is: A brief review of frequency histograms and relative frequency histograms as well. The density curve is symmetric and bell‑shaped. And this type of curve is something that we actually use in the statistics, and, as promised at the beginning of the video, this is the density curve we talk about.
A mathematical model for a probability distribution of a continuous random variable. The nd is symmetric — left and right sides are mirror images of each other. Idea of density density curve describes an overall pattern. The normal distribution is symmetric with scores more concentrated in the middle than in the tails. Learn about the importance of density curves and their properties. The standard normal density curve is the solid curve. All normal density curves satisfy the following property which is often referred to as the empirical rule. If showcurve=true, then a smoothed kernel density curve is displayed instead of a histogram. Which means that approximately 68.26 percent of the values lie in that range. The curve is symmetric about the mean. Large values of 𝜎yield graphs that are quite spread out. The density curve is symmetrical(i.e., an exact reflection of form on opposite sides of a dividing line), and centered about (divided by) its mean, with its the normal curve is a graph of the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and, as is the case with any continuous random. A normally distributed random variable, or a variable with a normal probability distribution, is a continuous random variable that has a relative this curve is also called the normal density curve.
What Is The Normal Density Curve Symmetric About?: The density curve is symmetrical(i.e., an exact reflection of form on opposite sides of a dividing line), and centered about (divided by) its mean, with its the normal curve is a graph of the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and, as is the case with any continuous random.